Abstract
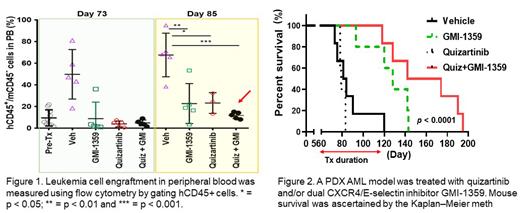
FLT3 inhibitors (FLT3i) have had transient success treating FLT3-mutant acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients, especially those with FLT3 internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutations that account for one-third of adult AML cases (Daver et al., 2021). However, FLT3i are typically ineffective in eliminating leukemia stem cells in the protective bone marrow (BM) microenvironmental "niche" (Borthakur et al., 2011; Cortes et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2008). Cytokines and chemokines such as CXCR4 and E-selectin ligands play a critical role in leukemia cell protection in the BM niche. Indeed, interactions of leukemic cells with their vicinal support cells, including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and endothelial cells (ECs), in the BM niche is mediated mainly through the CXCR4/SDF-1 and E-selectin/HECA-452/CD44 axes (Erbani et al., 2020; Peled and Tavor, 2013). Therefore, evaluation of the effects of FLT3i on CXCR4 and E-selectin signaling in leukemia cells could enhance our understanding of AML FLT3i resistance mechanisms. To this end, we investigated the levels of CXCR4 and E-selectin ligands on FLT3-ITD-mutated AML cells in vitro and in vivo during FLT3i treatment (e.g., quizartinib or sorafenib), and evaluated the anti-leukemia effects of CXCR4/E-selectin blockade with the dual inhibitor GMI-1359. We first checked the effects of FLT3i on the levels of CXCR4 and E-selectin ligands, as well as CD44, in vitro in human MOLM14 AML cells, which harbor FLT3-ITD mutations. All of these were upregulated, as measured by flow cytometry, following exposure to quizartinib (p < 0.001) or sorafenib (p < 0.01) for 96 h. The mRNA levels were also increased roughly 2-fold, as measured by qPCR, suggesting transcriptional regulation was involved in the upregulation. Further, the upregulation of CXCR4 and E-selectin ligands and CD44 was time dependent (from 2 to 96 h). FLT3i profoundly suppresses activation of ERK, AKT, and Stat5 (Zhang et al., 2008). Therefore, we tested if the suppression of each signaling pathways individually could upregulate of CXCR4. Unexpectedly, 72-h suppression of MEK/ERK signaling with selumetinib or pimasertib also upregulated CXCR4 in MOLM14 cells. No effects in this regard were observed by suppressing AKT/mTOR or Stat5 with AZD8055 or STAT5-IN-1, respectively. Additionally, in Dox-inducible NRAS (G12D)-mutated MOLM13 AML cells which also harbor FLT3 ITD mutations, ERK activation by doxycycline downregulated CXCR4 levels implying the MEK/ERK signaling pathway was associated with the suppression of CXCR4. Furthermore, under BM microenvironment-mimicking, co-culture using human MSCs/ECs and MOLM14 cells, blockade of CXCR4 and/or E-selectin signaling using the CXCR4 antagonist plerixafor, the E-selectin antagonist GMI-1271, or the CXCR4 and E-selectin dual inhibitor GMI-1359 showed that GMI-1359 markedly abrogated BM protection and sensitized MOLM14 cells to quizartinib-induced apoptosis. We further validated the effect of GMI-1359 in a PDX model of AML which were from a patient who relapsed from sorafenib+E6201+DAC in clinic and showed resistant to quizartinib ex vivo. The combination of GMI-1359 with quizartinib profoundly reduced leukemia burden and extended survival of the PDX mice compared to the vehicle or the single-agent treatments (median survival was 158 days vs. 82.5, 79 and 128 days, respectively, in combination group vs. vehicle, quizartinib and GMI-1359; p < 0.0001) [Figure 1,2]. Our results suggest that FLT3i can upregulate CXCR4 and E-selectin ligands and CD44 in FLT3-ITD leukemia cells, which is mediated, at least in part, via suppression of MEK/ERK signaling. GMI-1359 sensitized AML cells to quizartinib-induced apoptosis in vitro and statistically significantly extended AML PDX mouse survival in vivo. These findings provide a pre-clinical rational for using GMI-1359 to prevent or overcome FLT3i resistance when treating FLT3-mutant AML patients.
Fogler: GlycoMimetics Inc.: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Patents & Royalties. Magnani: GlycoMimetics Inc.: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Patents & Royalties. Konopleva: Eli Lilly: Patents & Royalties: intellectual property rights, Research Funding; Forty Seven: Other: grant support, Research Funding; KisoJi: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Other: grant support, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Grant Support, Research Funding; Ablynx: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: grant support, Research Funding; Reata Pharmaceuticals: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties: intellectual property rights; Rafael Pharmaceuticals: Other: grant support, Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-La Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: grant support; Calithera: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Sanofi: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Novartis: Other: research funding pending, Patents & Royalties: intellectual property rights; Agios: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Cellectis: Other: grant support; Stemline Therapeutics: Research Funding; Ascentage: Other: grant support, Research Funding. Andreeff: Senti-Bio: Consultancy; Daiichi-Sankyo: Consultancy, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Glycomimetics: Consultancy; Aptose: Consultancy; Novartis, Cancer UK; Leukemia & Lymphoma Society (LLS), German Research Council; NCI-RDCRN (Rare Disease Clin Network), CLL Foundation; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Research Funding; ONO Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Reata, Aptose, Eutropics, SentiBio; Chimerix, Oncolyze: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company; Medicxi: Consultancy; Oxford Biomedica UK: Research Funding; Breast Cancer Research Foundation: Research Funding; Syndax: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal